Blocking and deadlocks are two additional problems
that can appear with concurrent transactions.
They can cause major problems for a system and can slow and even halt performance.
These problems can be handled in the application,
or SQL Server will deal with them as best it can;
they will be described here only so that you will be aware of them and understand the concepts.
Avoiding and resolving blocking and deadlock issues
is the responsibility of the programmer.
* Blocking occurs when
one transaction is holding a lock on a resource
and a second transaction requires a conflicting lock type on that resource.
The second transaction must wait for the first transaction to release its lock
- in other words, it is blocked by the first transaction.
Cari Blog Ini
28 Juni 2012
Characteristics of an Effective Index
A good index helps you to retrieve your data by using fewer I/O operations
and system resources than a table scan.
Because an index scan requires traversing the tree to find an individual value,
using an index is not efficient when you are retrieving large amounts of data.
Note:
If a query accesses more than 20 percent of the rows in a table,
a table scan is more efficient than using an index.
An effective index retrieves only a few rows
- in fact, most queries end up using only a few rows anyway.
To perform effectively, an index should be designed with good selectivity.
The selectivity of an index is based on the number of rows per index key value.
An index with poor selectivity has multiple rows per index key value;
an index with good selectivity has a few rows or one row per index key value.
and system resources than a table scan.
Because an index scan requires traversing the tree to find an individual value,
using an index is not efficient when you are retrieving large amounts of data.
Note:
If a query accesses more than 20 percent of the rows in a table,
a table scan is more efficient than using an index.
An effective index retrieves only a few rows
- in fact, most queries end up using only a few rows anyway.
To perform effectively, an index should be designed with good selectivity.
The selectivity of an index is based on the number of rows per index key value.
An index with poor selectivity has multiple rows per index key value;
an index with good selectivity has a few rows or one row per index key value.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Types of Files that A Database Can Use
As mentioned, a SQL Server database is made up of a set of operating system files.
A database file can be either a data file or a log file.
Data files are used to store data and objects,
such as tables, indexes, views, triggers, and stored procedures.
There are two types of data files: primary and secondary.
Log files are used to store transaction log information only.
Log space is always managed separately from data space and can never be part of a data file.
Every database must be created with at least one data file and one log file,
and files may not be used by more than one database—that is, databases cannot share files.
The following list describes the three types of files that a database can use.
* Primary data file
A primary data file contains all of the startup information for the database
and its system tables and objects.
A database file can be either a data file or a log file.
Data files are used to store data and objects,
such as tables, indexes, views, triggers, and stored procedures.
There are two types of data files: primary and secondary.
Log files are used to store transaction log information only.
Log space is always managed separately from data space and can never be part of a data file.
Every database must be created with at least one data file and one log file,
and files may not be used by more than one database—that is, databases cannot share files.
The following list describes the three types of files that a database can use.
* Primary data file
A primary data file contains all of the startup information for the database
and its system tables and objects.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Types of Filegroups in Database
A simple database might have one primary data file,
which is large enough to hold all data and objects, and one transaction log file.
A more complex database might have one primary data file,
five secondary data files, and two transaction log files.
How, then, could the data be spread across all the data files?
The answer is that filegroups can be used to arrange data.
Filegroups enable you to group files for administrative and data placement purposes.
Filegroups can improve database performance
by allowing a database to be created across multiple disks, multiple disk controllers, or RAID systems.
You can create tables and indexes on specific disks by using filegroups, thus enabling you to direct the I/O
for a certain table or index to specific physical disks, controllers, or arrays of disks.
There are three types of filegroups.
The main characteristics of these filegroups are outlined in the following list:
which is large enough to hold all data and objects, and one transaction log file.
A more complex database might have one primary data file,
five secondary data files, and two transaction log files.
How, then, could the data be spread across all the data files?
The answer is that filegroups can be used to arrange data.
Filegroups enable you to group files for administrative and data placement purposes.
Filegroups can improve database performance
by allowing a database to be created across multiple disks, multiple disk controllers, or RAID systems.
You can create tables and indexes on specific disks by using filegroups, thus enabling you to direct the I/O
for a certain table or index to specific physical disks, controllers, or arrays of disks.
There are three types of filegroups.
The main characteristics of these filegroups are outlined in the following list:
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
When to Use Indexes
Indexes are best suited for tasks such as the following:
* Queries that specify a narrow search criteria
These queries should retrieve only a few rows that match the specific criteria.
* Queries that specify a range of values
These queries should also retrieve a small number of rows.
* Searches that are used in a join
Columns that are often used as join keys are good candidates for indexes.
* Queries that specify a narrow search criteria
These queries should retrieve only a few rows that match the specific criteria.
* Queries that specify a range of values
These queries should also retrieve a small number of rows.
* Searches that are used in a join
Columns that are often used as join keys are good candidates for indexes.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Full-Text Indexes
A SQL Server full-text index is actually more like a catalog than an index,
and its structure is not a B-tree.
The full-text index allows you to search by groups of keywords.
The full-text index is part of the Microsoft Search service;
it is used extensively in Web site search engines and in other text-based operations.
Unlike B-tree indexes,
a full-text index is stored outside the database but is maintained by the database. Because it is stored externally, the index can maintain its own structure.
The following restrictions apply to full-text indexes:
* A full-text index must include a column that uniquely identifies each row in the table.
and its structure is not a B-tree.
The full-text index allows you to search by groups of keywords.
The full-text index is part of the Microsoft Search service;
it is used extensively in Web site search engines and in other text-based operations.
Unlike B-tree indexes,
a full-text index is stored outside the database but is maintained by the database. Because it is stored externally, the index can maintain its own structure.
The following restrictions apply to full-text indexes:
* A full-text index must include a column that uniquely identifies each row in the table.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Types of B-tree Indexes
There are two types of B-tree indexes:
1. Clustered indexes
A clustered index stores the actual rows of data in its leaf nodes.
2. Nonclustered indexes.
A nonclustered index is an auxiliary structure that points to data in a table.
1. Clustered indexes
A clustered index stores the actual rows of data in its leaf nodes.
2. Nonclustered indexes.
A nonclustered index is an auxiliary structure that points to data in a table.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Example of Using Hints in Query Optimizer
When SQL Server Query Optimizer generates a query execution plan,
it chooses an index based on which index will provide the best performance
- usually the index that will use the fewest I/O operations and retrieve the least number of rows.
Although Query Optimizer usually chooses the most efficient query execution plan
and access path for your query, you might be able to do better
if you know more about your data than Query Optimizer does.
For example,
suppose you want to retrieve data about a person named "Smith"
from a table with a column listing last names.
Index statistics generalize based on a column.
Suppose the statistics show that each last name appears three times on average in the column.
This information provides fairly good selectivity;
however, you know that the name "Smith" appears much more often than average.
it chooses an index based on which index will provide the best performance
- usually the index that will use the fewest I/O operations and retrieve the least number of rows.
Although Query Optimizer usually chooses the most efficient query execution plan
and access path for your query, you might be able to do better
if you know more about your data than Query Optimizer does.
For example,
suppose you want to retrieve data about a person named "Smith"
from a table with a column listing last names.
Index statistics generalize based on a column.
Suppose the statistics show that each last name appears three times on average in the column.
This information provides fairly good selectivity;
however, you know that the name "Smith" appears much more often than average.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
How To Validate Availability of Stored Procedure in Database using EXISTS
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IF EXISTS
(
SELECT [name] FROM sysobjects
WHERE
[name]='sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop'
and type='P'
)
BEGIN
SELECT '-----Stored Procedure: sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop is available-----'
END
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----Stored Procedure: sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop is available-----
(1 row(s) affected)
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IF EXISTS
(
SELECT [name] FROM sysobjects
WHERE
[name]='sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop'
and type='P'
)
BEGIN
SELECT '-----Stored Procedure: sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop is available-----'
END
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----Stored Procedure: sp_PerTahun_Jumlah_Kelompok_Umur_Loop is available-----
(1 row(s) affected)
How To Validate Availability of Table in Database using EXISTS
1.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXEC
(
'if EXISTS (
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.tables
WHERE table_name = ''Cabang_1''
)
SELECT ''-----Table:Cabang_1 is available '' '
)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
----------------------------------
-----Table:Cabang_1 is available
(1 row(s) affected)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXEC
(
'if EXISTS (
select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.tables
WHERE table_name = ''Cabang_1''
)
SELECT ''-----Table:Cabang_1 is available '' '
)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
----------------------------------
-----Table:Cabang_1 is available
(1 row(s) affected)
How To Find Text in Table of Database
1. Create this procedure
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
create PROC SearchAllTables_Test
(
@SearchStr nvarchar(100)
)
AS
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE #Results (ColumnName nvarchar(370), ColumnValue nvarchar(3630))
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @TableName nvarchar(256), @ColumnName nvarchar(128), @SearchStr2 nvarchar(110)
SET @TableName = ''
SET @SearchStr2 = QUOTENAME('%' + @SearchStr + '%','''')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
create PROC SearchAllTables_Test
(
@SearchStr nvarchar(100)
)
AS
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE #Results (ColumnName nvarchar(370), ColumnValue nvarchar(3630))
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @TableName nvarchar(256), @ColumnName nvarchar(128), @SearchStr2 nvarchar(110)
SET @TableName = ''
SET @SearchStr2 = QUOTENAME('%' + @SearchStr + '%','''')
How To Check All Columns in Table of Database
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------
select
cast (ordinal_position as varchar(3))as Field,
cast(column_name as varchar(25)) as FieldName,
cast(data_type as varchar(15)) as Type,
cast(character_maximum_length as varchar(5)) as Width
from information_schema.columns
join sysobjects on sysobjects.name=information_schema.columns.table_name
where
xtype='u'
and type='u'
and table_name='MsKaryawan'
order by ordinal_position
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------
select
cast (ordinal_position as varchar(3))as Field,
cast(column_name as varchar(25)) as FieldName,
cast(data_type as varchar(15)) as Type,
cast(character_maximum_length as varchar(5)) as Width
from information_schema.columns
join sysobjects on sysobjects.name=information_schema.columns.table_name
where
xtype='u'
and type='u'
and table_name='MsKaryawan'
order by ordinal_position
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------
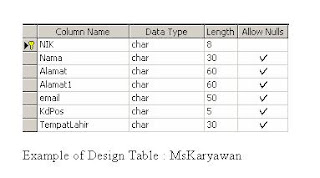
How To Check Primary Key of Table
1. Sample of Design Table
2. Display related columns
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------
SELECT
col.name
,col.colid
,col.isnullable
,typ.name
FROM syscolumns col
JOIN systypes typ on col.xtype=typ.xtype
WHERE id = OBJECT_ID('mskaryawan')
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------
2. Display related columns
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------------
SELECT
col.name
,col.colid
,col.isnullable
,typ.name
FROM syscolumns col
JOIN systypes typ on col.xtype=typ.xtype
WHERE id = OBJECT_ID('mskaryawan')
----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------------
Example of Workload Processing in An Active-Passive Server Setup
Each of these solutions uses one or more standby or "passive" servers,
which hold a replica of the main "active" database.
During normal processing,
the work-load is directed to the "active" server,
as shown in Figure 2-4a.
In the event of a failure of the "active" server,
the processing is transferred to the passive server and it becomes the active server,
as shown in Figure 2-4b.
which hold a replica of the main "active" database.
During normal processing,
the work-load is directed to the "active" server,
as shown in Figure 2-4a.
In the event of a failure of the "active" server,
the processing is transferred to the passive server and it becomes the active server,
as shown in Figure 2-4b.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
27 Juni 2012
Index Keys in Database
An index key designates the column or columns that are used to generate the index.
The index key is the value that enables you to quickly find the row
that contains the data you are interested in,
much like an index entry in a book points you to a particular topic in the text.
To access the data row by using the index,
you must include the index key value or values in the WHERE clause of the SQL statement.
How this is accomplished depends on whether the index is a simple index or a composite index.
A. Simple Indexes
A simple index is an index that is defined on only one table column,
as illustrated in Figure 17-4.
This column must be referenced in the WHERE clause of the SQL statement
in order for this index to be used to satisfy the statement.
The index key is the value that enables you to quickly find the row
that contains the data you are interested in,
much like an index entry in a book points you to a particular topic in the text.
To access the data row by using the index,
you must include the index key value or values in the WHERE clause of the SQL statement.
How this is accomplished depends on whether the index is a simple index or a composite index.
A. Simple Indexes
A simple index is an index that is defined on only one table column,
as illustrated in Figure 17-4.
This column must be referenced in the WHERE clause of the SQL statement
in order for this index to be used to satisfy the statement.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
What Is an Index in Database ?
As mentioned, an index is an auxiliary data structure used by SQL Server to access data.
Depending on its type, an index is stored with the data or separate from the data.
In systems without indexes, all data retrieval must be done by using table scans.
In a table scan, all of the data in a table must be read and compared with the requested data.
Table scans are generally avoided
because of the amount of I/O that is generated by this operations
- scanning large tables could take a long time and eat up a lot of system resources.
By using an index,
* you can greatly reduce the number of I/O operations,
* speeding up access to data as well as freeing up system resources for other operations.
Depending on its type, an index is stored with the data or separate from the data.
In systems without indexes, all data retrieval must be done by using table scans.
In a table scan, all of the data in a table must be read and compared with the requested data.
Table scans are generally avoided
because of the amount of I/O that is generated by this operations
- scanning large tables could take a long time and eat up a lot of system resources.
By using an index,
* you can greatly reduce the number of I/O operations,
* speeding up access to data as well as freeing up system resources for other operations.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Index Guidelines
You should follow a number of index guidelines
to increase both the efficiency and the performance of the system:
* Use indexes in moderation.
A few indexes can be quite useful,
but too many indexes can adversely affect the performance of the system.
Because the indexes must be maintained,
every time an insert, update, or delete operation is performed on the table,
the index must be updated.
If there are very many of these operations, the overhead of maintaining the index can be quite high.
* Don't index small tables.
It is sometimes much more efficient to perform table scans if the table is small (say, a few hundred rows).
The additional overhead of the index is not worth the benefit.
to increase both the efficiency and the performance of the system:
* Use indexes in moderation.
A few indexes can be quite useful,
but too many indexes can adversely affect the performance of the system.
Because the indexes must be maintained,
every time an insert, update, or delete operation is performed on the table,
the index must be updated.
If there are very many of these operations, the overhead of maintaining the index can be quite high.
* Don't index small tables.
It is sometimes much more efficient to perform table scans if the table is small (say, a few hundred rows).
The additional overhead of the index is not worth the benefit.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
What Is a Trigger in Database ?
* A trigger is a special type of stored procedure
that is executed automatically by SQL Server
when a table is modified by any one of the three statements:
UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE.
* Triggers, like other stored procedures,
can contain simple or complex T-SQL statements.
Unlike other types of stored procedures,
triggers execute automatically when specified data modifications occur
and cannot be executed manually by name.
* When a trigger executes, it is said to have fired.
A trigger is created on one database table,
but it can access other tables and objects in other databases.
* Triggers cannot be created on temporary tables or system tables,
only on user-defined tables or views. The table on which a trigger is defined is called a trigger table.
that is executed automatically by SQL Server
when a table is modified by any one of the three statements:
UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE.
* Triggers, like other stored procedures,
can contain simple or complex T-SQL statements.
Unlike other types of stored procedures,
triggers execute automatically when specified data modifications occur
and cannot be executed manually by name.
* When a trigger executes, it is said to have fired.
A trigger is created on one database table,
but it can access other tables and objects in other databases.
* Triggers cannot be created on temporary tables or system tables,
only on user-defined tables or views. The table on which a trigger is defined is called a trigger table.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Performance and Scalability for Database
When you develop an application and a database schema,
you should keep performance and scalability in mind.
You make many choices during the application design phase
that can eventually affect the performance and the scalability of the system.
These choices include the following:
* The use of temporary worktables
Often these tables are effective when the database is small,
but as the amount of data becomes larger and larger, they cease to function properly.
* The use of aggregate functions
The use of aggregate functions such as MIN(), MAX(), and AVG() scales with the amount of data used.
So be careful that your data set does not eventually become unwieldy.
* The use of indexes
As the amount of data grows, the use of indexes becomes much more important.
* The use of transactions
The use of explicit transactions is great for assuring that operations are atomic. However, as the number of concurrent users grows, it is important to reduce locking as much as possible.
you should keep performance and scalability in mind.
You make many choices during the application design phase
that can eventually affect the performance and the scalability of the system.
These choices include the following:
* The use of temporary worktables
Often these tables are effective when the database is small,
but as the amount of data becomes larger and larger, they cease to function properly.
* The use of aggregate functions
The use of aggregate functions such as MIN(), MAX(), and AVG() scales with the amount of data used.
So be careful that your data set does not eventually become unwieldy.
* The use of indexes
As the amount of data grows, the use of indexes becomes much more important.
* The use of transactions
The use of explicit transactions is great for assuring that operations are atomic. However, as the number of concurrent users grows, it is important to reduce locking as much as possible.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Determining How Much Space for Database
The process of determining how much space your database requires is fairly straightforward.
The amount of space is equal to the sum of the following:
* Space required for data
* Space required for indexes
* Space required for temporary data
* Space required for the transaction log
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
The amount of space is equal to the sum of the following:
* Space required for data
* Space required for indexes
* Space required for temporary data
* Space required for the transaction log
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Example Events Leading Up to The Failure and To Aid Recovery Using System Log
The system log is critical in the event of a system failure or performance degradation.
You can use the following information
to determine the sequence of events leading up to the failure and to aid recovery:
* Observations
An important part of the DBA's job
is to notice changes in the system and to anticipate problems.
Observations of unusual activity should be noted.
Even a note as simple as "The system seems sluggish"
might hold valuable clues in the event of a subsequent system failure.
* System changes
The DBA should record all changes made to the hardware,
the operating system, and the database system.
Entries should be in chronological order and should be complete but without unnecessary details.
You can use the following information
to determine the sequence of events leading up to the failure and to aid recovery:
* Observations
An important part of the DBA's job
is to notice changes in the system and to anticipate problems.
Observations of unusual activity should be noted.
Even a note as simple as "The system seems sluggish"
might hold valuable clues in the event of a subsequent system failure.
* System changes
The DBA should record all changes made to the hardware,
the operating system, and the database system.
Entries should be in chronological order and should be complete but without unnecessary details.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Variety of Types of Failure in Database
As a database administrator, your primary job is to keep the database up and running
during specific time periods, which are usually outlined in a service level agreement.
This service level agreement probably specifies the amount of uptime your system must provide,
as well as performance rates and recovery time in the event of a failure.
In fact, a variety of types of failures can occur in a complex computer system, including the following:
* Disk drive failure
Disk drive technology has improved,
but a disk drive is still a mechanical device and, as such, is subject to wear.
The disk drive is one of the most common areas of failure.
* Hardware component failure
Hardware failures can occur because of wear and tear on the components, primarily from heat.
Even the best-made computer equipment can fail over time.
during specific time periods, which are usually outlined in a service level agreement.
This service level agreement probably specifies the amount of uptime your system must provide,
as well as performance rates and recovery time in the event of a failure.
In fact, a variety of types of failures can occur in a complex computer system, including the following:
* Disk drive failure
Disk drive technology has improved,
but a disk drive is still a mechanical device and, as such, is subject to wear.
The disk drive is one of the most common areas of failure.
* Hardware component failure
Hardware failures can occur because of wear and tear on the components, primarily from heat.
Even the best-made computer equipment can fail over time.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Counters in Performance Monitor for Collecting Usage Data for Multiple CPUs
You can also retrieve system-averaged data for multiple CPUs via Performance Monitor.
Use the System object, which includes the following counters, among others:
* % Total Processor Time
Sum of the % Processor Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
* % Total Privileged Time
Sum of the % Privileged Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
* % Total User Time
Sum of the % User Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
Use the System object, which includes the following counters, among others:
* % Total Processor Time
Sum of the % Processor Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
* % Total Privileged Time
Sum of the % Privileged Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
* % Total User Time
Sum of the % User Times for each processor divided by the number of processors in the system.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Counters in Performance Monitor for Collecting Memory Usage Data
These counters include the following:
* Page Faults/sec
This counter contains the average number of page faults that occur in the system per second.
Remember that a page fault occurs
when a requested code or data page is not in working or standby memory.
* Cache Faults/sec
This counter contains the average number of cache faults that occur in the system per second.
Remember that cache faults occur
whenever the Cache Manager does not find a file's page in the immediate cache.
* Page Faults/sec
This counter contains the average number of page faults that occur in the system per second.
Remember that a page fault occurs
when a requested code or data page is not in working or standby memory.
* Cache Faults/sec
This counter contains the average number of cache faults that occur in the system per second.
Remember that cache faults occur
whenever the Cache Manager does not find a file's page in the immediate cache.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Counters in Performance Monitor for Collecting Disk Usage Data
Once the system is set up and operational,
you should collect disk usage data to keep apprised of any changes that might be necessary.
The system might expand to more users (and thus more transactions),
the requirement for the database might change (resulting in a larger database size), and so on.
When performing post-capacity planning studies on disk usage,
you should track the following counters in Performance Monitor.
These counters can be found in the [PhysicalDisk] object:
* % Disk Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing read or write requests.
* % Disk Read Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing read requests.
* % Disk Write Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing write requests.
you should collect disk usage data to keep apprised of any changes that might be necessary.
The system might expand to more users (and thus more transactions),
the requirement for the database might change (resulting in a larger database size), and so on.
When performing post-capacity planning studies on disk usage,
you should track the following counters in Performance Monitor.
These counters can be found in the [PhysicalDisk] object:
* % Disk Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing read or write requests.
* % Disk Read Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing read requests.
* % Disk Write Time
Percentage of elapsed time that the selected disk drive is busy servicing write requests.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Counters in Performance Monitor to Collecting Process Data
Process information can be valuable when you are profiling a workload activity.
Profiling a workload means determining what work each user is actually performing.
Performance Monitor provides a variety of counters for this purpose.
These counters are similar to the counters in the [Processor] object,
but in this case they are used to collect process data.
These counters can be found in the Process object and include the following:
* % Processor Time
Percentage of elapsed time during
which all of the threads of this process used the processor to execute instructions.
Code executed to handle certain hardware interrupts or trap conditions may be counted for this process.
* % User Time
Percentage of elapsed time this process's threads have spent executing code in User mode.
Profiling a workload means determining what work each user is actually performing.
Performance Monitor provides a variety of counters for this purpose.
These counters are similar to the counters in the [Processor] object,
but in this case they are used to collect process data.
These counters can be found in the Process object and include the following:
* % Processor Time
Percentage of elapsed time during
which all of the threads of this process used the processor to execute instructions.
Code executed to handle certain hardware interrupts or trap conditions may be counted for this process.
* % User Time
Percentage of elapsed time this process's threads have spent executing code in User mode.
Labels:
IT - SQL Server - Concept
Tips for Views in Database
When you are creating a view,
remember that a view is made up of an SQL statement that accesses the underlying data,
and that you control this SQL statement.
Also keep in mind the following guidelines,
which can help improve the performance, manageability, and usability of your databases:
* Use views for security.
Rather than re-creating a table to provide access to only certain data in the table, create a view that contains the columns and rows you want to make accessible.
Using a view is an ideal way to restrict some users to one portion of the data
and other users to a different portion of the data.
By using a view instead of building a table that must be populated from an existing table,
you do not increase the amount of data and you maintain security.
* Take advantage of indexes.
Remember that when you use a view,
you are still accessing the underlying tables and therefore the indexes on those tables.
If a table has a column that is indexed,
be sure to include that column in the WHERE clause of the view's SELECT statement.
Only if the column is part of the view
and is used in the WHERE clause can the index be used for selecting data.
remember that a view is made up of an SQL statement that accesses the underlying data,
and that you control this SQL statement.
Also keep in mind the following guidelines,
which can help improve the performance, manageability, and usability of your databases:
* Use views for security.
Rather than re-creating a table to provide access to only certain data in the table, create a view that contains the columns and rows you want to make accessible.
Using a view is an ideal way to restrict some users to one portion of the data
and other users to a different portion of the data.
By using a view instead of building a table that must be populated from an existing table,
you do not increase the amount of data and you maintain security.
* Take advantage of indexes.
Remember that when you use a view,
you are still accessing the underlying tables and therefore the indexes on those tables.
If a table has a column that is indexed,
be sure to include that column in the WHERE clause of the view's SELECT statement.
Only if the column is part of the view
and is used in the WHERE clause can the index be used for selecting data.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Information Sharing for DBA - Database Administrator
The DBA might be called upon to act as a consultant to developers, designers, and end users.
This consulting might include the following tasks:
* Assisting end users individually with specific problems,
developing a training curriculum, or even teaching that curriculum.
In many cases, ad hoc SQL is used as well as packaged queries for decision support systems (DSSs).
* Providing developers with information
about how the system has been used in the past and how new development can benefit users.
This discussion might precede informing users
about new tables and indexes available to them
as well as any other new features users might find handy.
* Providing designers with input about how different design features can benefit users.
The application that designers have developed might lack some features that the users want or need.
Passing this information to developers can help future development.
You are the most likely person for the users to come to with questions about how to use certain features, which makes you a good source of feedback to developers.
This consulting might include the following tasks:
* Assisting end users individually with specific problems,
developing a training curriculum, or even teaching that curriculum.
In many cases, ad hoc SQL is used as well as packaged queries for decision support systems (DSSs).
* Providing developers with information
about how the system has been used in the past and how new development can benefit users.
This discussion might precede informing users
about new tables and indexes available to them
as well as any other new features users might find handy.
* Providing designers with input about how different design features can benefit users.
The application that designers have developed might lack some features that the users want or need.
Passing this information to developers can help future development.
You are the most likely person for the users to come to with questions about how to use certain features, which makes you a good source of feedback to developers.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Variety Forms of Online Transaction Processing - OLTP
OLTP systems are characterized by many users accessing online data simultaneously.
In addition, and probably of more importance,
these users are waiting for a response from the system.
OLTP systems take a variety of forms, such as the following:
* Online purchasing
These applications are widely used because Internet commerce is growing rapidly.
When purchasing products over the Internet,
users often experience a delay while data is transmitted,
as well as while it is retrieved and processed.
By minimizing the database access time,
you improve the entire transaction time.
In addition, and probably of more importance,
these users are waiting for a response from the system.
OLTP systems take a variety of forms, such as the following:
* Online purchasing
These applications are widely used because Internet commerce is growing rapidly.
When purchasing products over the Internet,
users often experience a delay while data is transmitted,
as well as while it is retrieved and processed.
By minimizing the database access time,
you improve the entire transaction time.
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Components of Database Application
Each database application is divided into three distinct components.
These components are as follows:
* Database services
This is the back-end database server and the data that resides in the database.
* Application services
This is the application or business logic that manipulates the data that is retrieved from the database.
* Presentation services
This is the user interface.
The presentation services must be able to manipulate the data into an understandable form.
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
These components are as follows:
* Database services
This is the back-end database server and the data that resides in the database.
* Application services
This is the application or business logic that manipulates the data that is retrieved from the database.
* Presentation services
This is the user interface.
The presentation services must be able to manipulate the data into an understandable form.
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Example of Business Questions Related with Decision Support Systems - DSS
Decision support systems assist the user in making important business decisions
by providing a specific result based on a business question.
Here are a few examples of business questions
that might be answered by a decision support system:
* Who are the top salespeople in each district;
what are their best-selling products?
* What time of year does each product sell best?
* What was the result of lowering the price of an item?
* What is the average commission for salespeople by district?
by providing a specific result based on a business question.
Here are a few examples of business questions
that might be answered by a decision support system:
* Who are the top salespeople in each district;
what are their best-selling products?
* What time of year does each product sell best?
* What was the result of lowering the price of an item?
* What is the average commission for salespeople by district?
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
Example Tasks of Batch Processing Systems
Batch processing systems process offline jobs that do not have any end-user component.
The following tasks are typical jobs for this kind of system:
* Daily refresh of data
Some decision support systems require data to be reloaded every night,
and batch processing systems often automate this task.
* Data transformation
This task is similar to data refresh, but the data is transformed.
* Data cleansing
This task accomplishes things like removing duplicate accounts from the database.
* Offline billing
This task could consist of performing nightly billing of customers.
Batch processing systems typically have no users waiting for their jobs to finish,
but they also typically have a certain time frame in which they must conclude the tasks.
For example, overnight loads of data cannot overlap morning logins.
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
The following tasks are typical jobs for this kind of system:
* Daily refresh of data
Some decision support systems require data to be reloaded every night,
and batch processing systems often automate this task.
* Data transformation
This task is similar to data refresh, but the data is transformed.
* Data cleansing
This task accomplishes things like removing duplicate accounts from the database.
* Offline billing
This task could consist of performing nightly billing of customers.
Batch processing systems typically have no users waiting for their jobs to finish,
but they also typically have a certain time frame in which they must conclude the tasks.
For example, overnight loads of data cannot overlap morning logins.
Source:
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Administrator's Companion eBook
Labels:
IT - Database - Concept
21 Juni 2012
20 Juni 2012
How To Import Data From File Excel To SQL Using OpenRowSet
1. Sample of data
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
005 BSD
002 JAYAKARTA
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
005 BSD
002 JAYAKARTA
OLE/DB Provider 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0' IDBInitialize::Initialize returned 0x80004005
Error Messages :
Server: Msg 7399, Level 16, State 1, Line 1
OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0' reported an error.
The provider did not give any information about the error.
OLE DB error trace
[OLE/DB Provider 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0' IDBInitialize::Initialize returned 0x80004005:
The provider did not give any information about the error.].
* * * * *
OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0' Supplied Invalid Metadata For Column
Error Messages :
OLE DB provider 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0' supplied invalid metadata for column 'KdCabang'.
The data type is not supported.
OLE DB error trace
[Non-interface error: Column 'KdCabang' (ordinal 1) of object
'SELECT KdCabang, Cabang FROM [Sheet1$]'
reported an unsupported value for DBTYPE of 0].
* * * * *
19 Juni 2012
How To Export Data From SQL To New File Excel
1. Sample of data
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
005 BSD
002 JAYAKARTA
How To Export Data From SQL To Existing File Excel Using OpenRowSet
1. Sample of data
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
005 BSD
002 JAYAKARTA
003 KEBON JERUK
004 KELAPA GADING
Example How To Select Each Record in SQL Using Cursor
1. Sample data
--------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
--------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------
select * from Cabang
--------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------
Result Messages:
KdCabang Cabang
-------- ------------------------------
How To Loop Number in SQL Using Cursor
Example, want to loop number from 1 to 10
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------
declare @CounterNum int
declare CounterNumCursor cursor for
select 1 CounterNum
open CounterNumCursor
fetch CounterNumCursor into @CounterNum
while (@CounterNum <= 10 )
Begin
print @CounterNum
set @CounterNum=@CounterNum+1
fetch CounterNumCursor into @CounterNum
End
close CounterNumCursor
deallocate CounterNumCursor
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------
declare @CounterNum int
declare CounterNumCursor cursor for
select 1 CounterNum
open CounterNumCursor
fetch CounterNumCursor into @CounterNum
while (@CounterNum <= 10 )
Begin
print @CounterNum
set @CounterNum=@CounterNum+1
fetch CounterNumCursor into @CounterNum
End
close CounterNumCursor
deallocate CounterNumCursor
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
------------------------------------------------------------
How To Search Some Text in Stored Procedure
Example, want to search where is stored procedure that have this text
"select * into _Temp_SaldoCuti" ?
-----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
-----------------------------------------------------------
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(id)
FROM syscomments
WHERE [text] LIKE '%select * into _Temp_SaldoCuti%'
AND OBJECTPROPERTY(id, 'IsProcedure') = 1
GROUP BY OBJECT_NAME(id)
-----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
-----------------------------------------------------------
"select * into _Temp_SaldoCuti" ?
-----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
-----------------------------------------------------------
SELECT OBJECT_NAME(id)
FROM syscomments
WHERE [text] LIKE '%select * into _Temp_SaldoCuti%'
AND OBJECTPROPERTY(id, 'IsProcedure') = 1
GROUP BY OBJECT_NAME(id)
-----------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
-----------------------------------------------------------
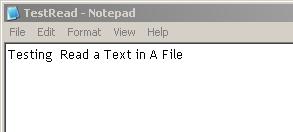
How To Copy File .txt to New File Using VB Script
1. Prepare a sample file, example : "TestRead.txt"
2. Copy this code, in new file :
'--------------------------------------------------------------
'-----code:start
'--------------------------------------------------------------
Dim arrFileLines()
i = 1
2. Copy this code, in new file :
'--------------------------------------------------------------
'-----code:start
'--------------------------------------------------------------
Dim arrFileLines()
i = 1
Example of Create Function in SQL with Returns Value
1.A. Create Function with parameter
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------
CREATE Function [Rate_Discount] (@Discount_1 as float,@Rate as float,@OGross as float)
RETURNS Float
AS
BEGIN
Declare @Discount Float
Select @Discount= (@Discount_1*@Rate)/(@OGross*@Rate+@Discount_1*@Rate)*100
if @Discount is null
Select @Discount=0
return(@Discount)
End
Example of Create Function (No Parameter) in SQL with Returns Value
1.A. Create Function with no parameter
------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------
CREATE Function [Rate_Discount] ()
RETURNS Float
AS
BEGIN
Declare @Discount Float
Select @Discount= (1000 / 0.27)
if @Discount is null
Select @Discount=0
return(@Discount)
End
Bimbisara, Raja Penyantun Yang Pertama
bersedia menerima dana makanan esok hari dari saya.
Raja Bimbisara juga mempersembahkan Hutan Bambu kepada Sang Buddha,
yang dimana hutan itu cocok sebagai tempat tinggal Para Bhikkhu,
dan Sang Buddha melewatkan masa vassa
yang kedua, ketiga, keempat, ketujuh belas dan kedua puluh
di Vihara Hutan Bambu tersebut.
* * * * *
Labels:
for Kid Kit
13 Juni 2012
Error SQL: Could not locate entry in sysdatabases
Error Messages :
Server: Msg 911, Level 16, State 1
[Microsoft][ODBC SQL Server Driver][SQL Server]
Could not locate entry in sysdatabases for database
‘HRD’.
No entry found with that name.
Make sure that the name is entered correctly.
ODBC SQLState: 420000 - RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally
Error Messages:
Microsoft SQL-DMO (ODBC SQLState: 420000)
Exclusive access could not be obtained because the database is in use.
RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Example of Restore Database with Attach and Detach Database Using Syntax SQL
/* Task for : Detach DB */
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [DB_Test]
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'DB_Test'
GO
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
--------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [DB_Test]
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'DB_Test'
GO
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Example of Restore Database Using Syntax SQL
/* Task for : Restore Database */
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
RESTORE DATABASE [DB_Test]
FROM DISK = N'\\xxx.xxx.x.44\Share\RestoreDB\DB_Test_120613_1340.DAT'
WITH FILE = 1,
MOVE N'DB_Test'
TO N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test.mdf',
MOVE N'DB_Test_Log'
TO N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test_Log.ldf',
NOUNLOAD,
REPLACE,
STATS = 10
GO
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
RESTORE DATABASE [DB_Test]
FROM DISK = N'\\xxx.xxx.x.44\Share\RestoreDB\DB_Test_120613_1340.DAT'
WITH FILE = 1,
MOVE N'DB_Test'
TO N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test.mdf',
MOVE N'DB_Test_Log'
TO N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test_Log.ldf',
NOUNLOAD,
REPLACE,
STATS = 10
GO
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
Example of Attach Database Using Syntax SQL
/* Task for : Attach DB */
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [DB_Test] ON
( FILENAME = N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test.mdf' ),
( FILENAME = N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test_log.ldf' )
FOR ATTACH
GO
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
CREATE DATABASE [DB_Test] ON
( FILENAME = N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test.mdf' ),
( FILENAME = N'C:\DBTest\DB_Test_log.ldf' )
FOR ATTACH
GO
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
Example of Detach Database Using Syntax SQL - sp_detach_db
/* Task for : Detach DB */
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [DB_Test]
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'DB_Test'
GO
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
--------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------------
USE [master]
GO
ALTER DATABASE [DB_Test]
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE
GO
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_detach_db @dbname = N'DB_Test'
GO
--------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Backup Database and Copying File To Another Server
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Declare
@Backup as varchar(100),
@BackupFile as varchar(100)
select @BackupFile='DB_Test'
+'_'+ convert(varchar(20),getdate(),12)
+'_'+ replace (CONVERT(VARCHAR(5),GETDATE(),108), ':', '')+'.dat'
select @Backup='C:\Backup_DBTest\'+@BackupFile
backup database [DB_Test] to DISK=@Backup
-----code:start
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Declare
@Backup as varchar(100),
@BackupFile as varchar(100)
select @BackupFile='DB_Test'
+'_'+ convert(varchar(20),getdate(),12)
+'_'+ replace (CONVERT(VARCHAR(5),GETDATE(),108), ':', '')+'.dat'
select @Backup='C:\Backup_DBTest\'+@BackupFile
backup database [DB_Test] to DISK=@Backup
Copy File Using Syntax SQL Command Shell - xp_cmdshell
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
Declare @CopyCommand as varchar(200)
select
@CopyCommand= 'Copy \\xxx.xxx.x.41\Share\DB_Test_120613_1319.dat '
+ ' \\xxx.xxx.x.44\Share\BackupDB\'
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell @CopyCommand, NO_OUTPUT
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
Declare @CopyCommand as varchar(200)
select
@CopyCommand= 'Copy \\xxx.xxx.x.41\Share\DB_Test_120613_1319.dat '
+ ' \\xxx.xxx.x.44\Share\BackupDB\'
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell @CopyCommand, NO_OUTPUT
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:end
----------------------------------------------------
Backup Database Using Syntax
----------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
Declare
@Backup as varchar(100)
,@BackupFile as varchar(100)
select
@BackupFile='DB_Test'
+'_'+ convert(varchar(20),getdate(),12)
+'_'+ replace(CONVERT(VARCHAR(5),GETDATE(),108), ':', '')+'.dat'
-----code:start
----------------------------------------------------
Declare
@Backup as varchar(100)
,@BackupFile as varchar(100)
select
@BackupFile='DB_Test'
+'_'+ convert(varchar(20),getdate(),12)
+'_'+ replace(CONVERT(VARCHAR(5),GETDATE(),108), ':', '')+'.dat'
Example of Shrink Database
--------------------------------------------------------------
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------
USE [HRD]
GO
-- Truncate the log by changing the database recovery model to SIMPLE.
ALTER DATABASE [HRD]
SET RECOVERY SIMPLE;
GO
-- Shrink the truncated log file to 1 MB.
DBCC SHRINKFILE (HRD_Data);
GO
DBCC SHRINKFILE (HRD_Log, 1);
GO
-----code:start
--------------------------------------------------------------
USE [HRD]
GO
-- Truncate the log by changing the database recovery model to SIMPLE.
ALTER DATABASE [HRD]
SET RECOVERY SIMPLE;
GO
-- Shrink the truncated log file to 1 MB.
DBCC SHRINKFILE (HRD_Data);
GO
DBCC SHRINKFILE (HRD_Log, 1);
GO
Backup and Restore Database Using Maintenance Plans
Applies To:
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
Tasks:
Backup Database and Restore using Maintenance Plans.
Example:
* Backup Database “DB_Test”
from Server “IT107\SQLSVR_1” to Local Drive
-> Maintenance Plan Name : Backup
* Restore file backup, to Database “DB_Test_Simulasi”
in Server “IT107\SQLSVR_2”
-> Maintenance Plan Name : Restore
For download a file .pdf, please open this link:
https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B6a5vK3IVP_0blFobTJQaHE2aVk
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
Tasks:
Backup Database and Restore using Maintenance Plans.
Example:
* Backup Database “DB_Test”
from Server “IT107\SQLSVR_1” to Local Drive
-> Maintenance Plan Name : Backup
* Restore file backup, to Database “DB_Test_Simulasi”
in Server “IT107\SQLSVR_2”
-> Maintenance Plan Name : Restore
For download a file .pdf, please open this link:
https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B6a5vK3IVP_0blFobTJQaHE2aVk
12 Juni 2012
“The system cannot find the file specified” When Using xp_cmdshell
Apply To :
Microsoft SQL Server 2000
Error Messages :
Microsoft SQL Server 2000
Error Messages :
The system cannot find the file specified. When using xp_cmdshell.
Copy All Files Between Certain Dates using Visual Basic
'-----code:start
Private Sub Copy_Files_Dates_Click()
'This example copy all files between certain dates from FromPath to ToPath.
'You can also use this to copy the files from the last ? days
'If Fdate >= Date - 30 Then
'Note: If the files in ToPath already exist it will overwrite
'existing files in this folder
Dim FSO As Object
Dim FromPath As String
Dim ToPath As String
Dim Fdate As Date
Dim FileInFromFolder As Object
Private Sub Copy_Files_Dates_Click()
'This example copy all files between certain dates from FromPath to ToPath.
'You can also use this to copy the files from the last ? days
'If Fdate >= Date - 30 Then
'Note: If the files in ToPath already exist it will overwrite
'existing files in this folder
Dim FSO As Object
Dim FromPath As String
Dim ToPath As String
Dim Fdate As Date
Dim FileInFromFolder As Object
Labels:
IT - - How To or Guide
08 Juni 2012
Copy and Rename One File Using Visual Basic
-----code:start
Sub Copy_One_File()
FileCopy "C:\Users\SourceFolder\Test.xls", "C:\Users\DestFolder\Test.xls"
End Sub
Sub Move_Rename_One_File()
'You can change the path and file name
Name "C:\Users\SourceFolder\Test.xls" As "C:\Users\DestFolder\TestNew.xls"
End Sub
-----code:start
Source:
http://www.rondebruin.nl/folder.htm
Sub Copy_One_File()
FileCopy "C:\Users\SourceFolder\Test.xls", "C:\Users\DestFolder\Test.xls"
End Sub
Sub Move_Rename_One_File()
'You can change the path and file name
Name "C:\Users\SourceFolder\Test.xls" As "C:\Users\DestFolder\TestNew.xls"
End Sub
-----code:start
Source:
http://www.rondebruin.nl/folder.htm
Labels:
IT - - How To or Guide
Copy Folder Using Visual Basic
Sub Copy_Folder()
'This example copy all files and subfolders from FromPath to ToPath.
'Note: If ToPath already exist it will overwrite existing files in this folder
'if ToPath not exist it will be made for you.
Dim FSO As Object
Dim FromPath As String
Dim ToPath As String
FromPath = "C:\Users\Data" '<< Change
ToPath = "C:\Users\Test" '<< Change
'If you want to create a backup of your folder every time you run this macro
'you can create a unique folder with a Date/Time stamp.
'ToPath = "C:\Users\" & Format(Now, "yyyy-mm-dd h-mm-ss")
'This example copy all files and subfolders from FromPath to ToPath.
'Note: If ToPath already exist it will overwrite existing files in this folder
'if ToPath not exist it will be made for you.
Dim FSO As Object
Dim FromPath As String
Dim ToPath As String
FromPath = "C:\Users\Data" '<< Change
ToPath = "C:\Users\Test" '<< Change
'If you want to create a backup of your folder every time you run this macro
'you can create a unique folder with a Date/Time stamp.
'ToPath = "C:\Users\" & Format(Now, "yyyy-mm-dd h-mm-ss")
Labels:
IT - - How To or Guide
06 Juni 2012
Kewajiban Anak Terhadap Orang Tua ( Dan Mertua )
Di dalam Sigalovada Sutta tertera :
"Dengan 5 ( lima ) cara seorang memperlakukan Orangtua-nya
sebagai Arah Timur :
1.)
Dahulu aku telah dipelihara atau dibesarkan oleh mereka, sekarang aku akan menyokong mereka
2.)
2.)
Aku akan melakukan tugas-tugas kewajiban-ku terhadap mereka
3.)
Aku akan menjaga baik-baik garis keturunan dan tradisi keluarga.
4.)
Aku akan membuat diri-ku pantas untuk menerima warisan.
5.)
Aku akan mengurus persembahyangan kepada sanak keluarga-ku yang telah meninggal dunia."
Untuk lebih lengkapnya, dapat di-download pada link berikut ini:
https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B6a5vK3IVP_0bFcyOXRObVhzbnM
( Digha Nikaya III, 189 )
Untuk lebih lengkapnya, dapat di-download pada link berikut ini:
https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B6a5vK3IVP_0bFcyOXRObVhzbnM
Sumber :
http://www.samaggi-phala.or.id
Bakti Kepada Orang Tua
Jasa Orang tua amat besar dan sulit terbalas oleh Anak-anak-nya selama hidupnya.
Dalam Anguttara Nikaya Bab IV Ayat 2
Sang Buddha memberikan perumpamaan sebagai berikut :
"Bila Seorang Anak menggendong Ayah-nya di pundak kiri
dan Ibu-nya di pundak kanan selama seratus tahun,
maka Anak tersebut belum cukup membalas
Jasa Kebaikan yang mendalam dari Orang Tua-nya."
https://docs.google.com/open?id=0B6a5vK3IVP_0aThwWmV3NF9ld00
04 Juni 2012
Kecantikan Hanya Setipis Kulit Batasnya
Permaisuri Raja Bimbisara bernama, Ratu Khema,
amat memuja kecantikan wajahnya.
Ratu Khema telah mengucapkan permohonannya di kaki Buddha Padumuttara,
ia ingin sekali mempunyai rupa dan wajah yang cantik.
Tetapi ia mendengar bahwa Sang Buddha Gotama mengatakan,
kecantikan bukan merupakan hal yang utama.
Pada kelahiran-kelahirannya yang terdahulu,
Ratu Khema selalu menjadi wanita yang amat cantik.
Raja Bimbisara yang mengetahui bahwa Istrinya amat mengagumi kecantikan wajahnya
lalu meminta pengarang lagu
untuk menciptakan lagu yang memuji keindahan hutan Veluvana.
Lagu itu kemudian dinyanyikan oleh para penyanyi terkenal.
amat memuja kecantikan wajahnya.
Ratu Khema telah mengucapkan permohonannya di kaki Buddha Padumuttara,
ia ingin sekali mempunyai rupa dan wajah yang cantik.
Tetapi ia mendengar bahwa Sang Buddha Gotama mengatakan,
kecantikan bukan merupakan hal yang utama.
Pada kelahiran-kelahirannya yang terdahulu,
Ratu Khema selalu menjadi wanita yang amat cantik.
Raja Bimbisara yang mengetahui bahwa Istrinya amat mengagumi kecantikan wajahnya
lalu meminta pengarang lagu
untuk menciptakan lagu yang memuji keindahan hutan Veluvana.
Lagu itu kemudian dinyanyikan oleh para penyanyi terkenal.
Bakti Kepada Ayah dan Ibu
Sesungguhnya,
mendukung maupun menyokong Ayah dan Ibu
adalah Berkah Utama
karena dapat memberikan Kebahagiaan untuk kedua belah pihak.
Ketika Anak mampu mengenalkan serta meyakinkan Orangtua
agar selalu melaksanakan Buddha Dhamma,
maka Jasa Kebajikan Anak mampu melebihi Jasa Kebajikan
yang pernah Orangtua lakukan terhadap Anak.
* * * * *
03 Juni 2012
Persahabatan yang Baik
Dan bagaimana seorang perumah-tangga mantap dalam
* keyakinan
* moralitas
* kedermawanan
* kebijaksanaan
* * * * * * * * * *
Di Anguttara Nikaya 8.54, dijelaskan tentang persahabatan yang baik sebagai berikut:
Dan apakah persahabatan yang baik itu?
Labels:
Dhamma - Keluarga
Perbuatan yang Menjamin Keberhasilan
Demikian yang telah Saya dengar:
Suatu ketika Sang Buddha berdiam di dekat Savatthi, di Hutan Jeta di Vihara Anathapindika.
Pada suatu malam yang indah,
datang-lah Dewa dengan cahaya cemerlang yang menerangi seluruh Hutan Jeta.
Dia mendatangi Sang Buddha, memberikan Hormat,
lalu berdiri di satu sisi dan berkata kepada Sang Buddha dalam syair berikut ini:
Banyak Dewa dan Manusia, karena menginginkan Kesejahteraan,
telah merenungkan apa Perbuatan yang menjanjikan Keberhasilan.
Suatu ketika Sang Buddha berdiam di dekat Savatthi, di Hutan Jeta di Vihara Anathapindika.
Pada suatu malam yang indah,
datang-lah Dewa dengan cahaya cemerlang yang menerangi seluruh Hutan Jeta.
Dia mendatangi Sang Buddha, memberikan Hormat,
lalu berdiri di satu sisi dan berkata kepada Sang Buddha dalam syair berikut ini:
Banyak Dewa dan Manusia, karena menginginkan Kesejahteraan,
telah merenungkan apa Perbuatan yang menjanjikan Keberhasilan.
Terangkan-lah apakah Perbuatan Tertinggi yang menjamin Keberhasilan itu ?
Labels:
Dhamma - Manfaat
Menggunakan Kekayaan secara Benar
A. Apakah kemantapan dalam Keyakinan itu ?
B. Apakah kemantapan dalam Moralitas itu ?
C. Apakah kemantapan dalam Kedermawanan itu ?
D. Apakah kemantapan dalam Kebijaksanaan itu ?
* * *
"Dengan kekayaan yang telah diperoleh lewat usaha yang penuh semangat,
dikumpulkan dengan kekuatan tangan-nya,
didapatkan dengan keringat di dahi-nya,
kekayaan benar yang telah diperoleh secara benar,
Siswa yang Luhur mengambil empat tindakan yang pantas.
Apakah yang empat itu ?
* * * * *
Labels:
Dhamma - Manfaat
Dana Makanan
Pada suatu ketika Sang Buddha berdiam di antara Suku Koliya, di kota Sajjanela.
Suatu pagi Sang Buddha mengenakan pakaian,
mengambil jubah atas dan mangkuk-Nya, dan pergi ke tempat tinggal Suppavasa,
Seorang Wanita Koliya.
Setelah tiba di sana, Beliau duduk di tempat yang telah disediakan.
Suppavasa, Wanita Koliya itu melayani Beliau secara pribadi
dan menyajikan berbagai makanan yang lezat.
Setelah Sang Buddha selesai makan dan telah menarik tangan-Nya dari mangkuk,
Suppavasa, Wanita Koliya itu duduk di satu sisi, dan Sang Buddha berkata:
Suatu pagi Sang Buddha mengenakan pakaian,
mengambil jubah atas dan mangkuk-Nya, dan pergi ke tempat tinggal Suppavasa,
Seorang Wanita Koliya.
Setelah tiba di sana, Beliau duduk di tempat yang telah disediakan.
Suppavasa, Wanita Koliya itu melayani Beliau secara pribadi
dan menyajikan berbagai makanan yang lezat.
Setelah Sang Buddha selesai makan dan telah menarik tangan-Nya dari mangkuk,
Suppavasa, Wanita Koliya itu duduk di satu sisi, dan Sang Buddha berkata:
"Dengan memberikan makanan,
Suppavasa - Seorang Siswa Wanita yang Luhur - memberikan empat hal kepada Penerima-nya.
Apakah yang empat itu ?
Labels:
Dhamma - Manfaat
Manfaat Mendengarkan Dhamma atau Membaca Sutta
Mengapa perlu mendengarkan Dhamma atau membaca Sutta ?
Anguttara Nikaya 5.202 menjelaskan Lima Manfaat dari mendengarkan Dhamma (membaca Sutta) yakni:
1. Mendengar atau mengetahui apa yang belum pernah didengar atau diketahui sebelum-nya
2. Memastikan apa yang sudah didengar atau diketahui sebelum-nya
3. Menghilangkan keraguan
4. Memperoleh Pandangan Benar
5. Batin menjadi tenang
Labels:
Dhamma - Manfaat
Istanavihara - Kisah Visakha Berdana Istana
Yang Terberkahi sedang berdiam di Savatthi di Jetavana.
Pada waktu itu, Visakha, umat awam agung itu,
telah dibujuk oleh teman-teman dan pelayan-pelayannya
untuk berjalan-jalan di taman pada suatu hari perayaan.
Setelah mandi dan diminyaki dengan baik, dia menyantap makanan yang enak,
menghias diri dengan seperangkat hiasan "perambat besar".
Lalu, dengan dikelilingi lima ratus pendamping,
dia berangkat dari rumah dengan upacara besar dan dengan sejumlah besar pengikut.
Sementara berjalan menuju taman itu, Visakha berpikir,
"Apa yang ada bagiku di sana, di dalam hiburan kosong seolah-olah saya adalah gadis muda?
Sebaiknya saya pergi ke vihara, memberi hormat kepada Yang Terberkahi
dan para pria mulia yang memberikan inspirasi pada pikiran,
dan saya akan mendengarkan Dhamma."
Maka dia pergi ke vihara, berhenti di satu sisi,
melepaskan perhiasan "perambat besar", dan memberikannya ke tangan seorang pelayan.
Lalu, dengan khusuk dia memberi penghormatan kepada Yang Terberkahi,
dan duduk di satu sisi.
Dia mendengarkan Dhamma, dan melakukan ucapara mengelilingi Sang Buddha,
dan kemudian meninggalkan vihara.
Pada waktu itu, Visakha, umat awam agung itu,
telah dibujuk oleh teman-teman dan pelayan-pelayannya
untuk berjalan-jalan di taman pada suatu hari perayaan.
Setelah mandi dan diminyaki dengan baik, dia menyantap makanan yang enak,
menghias diri dengan seperangkat hiasan "perambat besar".
Lalu, dengan dikelilingi lima ratus pendamping,
dia berangkat dari rumah dengan upacara besar dan dengan sejumlah besar pengikut.
Sementara berjalan menuju taman itu, Visakha berpikir,
"Apa yang ada bagiku di sana, di dalam hiburan kosong seolah-olah saya adalah gadis muda?
Sebaiknya saya pergi ke vihara, memberi hormat kepada Yang Terberkahi
dan para pria mulia yang memberikan inspirasi pada pikiran,
dan saya akan mendengarkan Dhamma."
Maka dia pergi ke vihara, berhenti di satu sisi,
melepaskan perhiasan "perambat besar", dan memberikannya ke tangan seorang pelayan.
Lalu, dengan khusuk dia memberi penghormatan kepada Yang Terberkahi,
dan duduk di satu sisi.
Dia mendengarkan Dhamma, dan melakukan ucapara mengelilingi Sang Buddha,
dan kemudian meninggalkan vihara.
Labels:
Dhamma
Kelahirannya Sebagai Raja Shibi
Beliau mendengarkan permintaan mereka seolah mendengar sebuah kabar gembira.
Kebahagiaan Para Pengemis bahkan melampaui kebahagiaan Sang Raja sendiri,
mereka menyebarluaskan kabar gembira kemurahan hati Sang Raja ke seluruh negeri di sekelilingnya.
Kebahagiaan Para Pengemis bahkan melampaui kebahagiaan Sang Raja sendiri,
mereka menyebarluaskan kabar gembira kemurahan hati Sang Raja ke seluruh negeri di sekelilingnya.
Mengingat bahwa kalian telah melihat mataku, mata yang memiliki kekuatan Dewa,
yang diperoleh dari Kebajikan beramal dana.
* * *
Harta sesungguhnya tak berarti begitu saja,
hingga ia menjadi Kebajikan seseorang;
Ia dapat diberikan bagi Kebajikan yang lain.
Hanya dengan sikap yang demikianlah Ia akan menjadi harta karun;
* * * * *
Labels:
Cerita - Sang Buddha
Kisah tentang Unmadayanti - Unmadayanti Jataka
Dan karena Aku senantiasa memikirkan Kebajikan Rakyatku,
Aku harus terus mencintai Jalan Kebajikan, sejalan dengan ketenaranku.
Sebagaimana lembu yang mengikuti Pemimpin kawanan ke mana pun,
benar atau salah, demikianlah agar Rakyat meniru Pemimpinnya tanpa merasa terpaksa.
Aku harus terus mencintai Jalan Kebajikan, sejalan dengan ketenaranku.
Sebagaimana lembu yang mengikuti Pemimpin kawanan ke mana pun,
benar atau salah, demikianlah agar Rakyat meniru Pemimpinnya tanpa merasa terpaksa.
* * *
Orang yang baik senantiasa merasa enggan untuk mengikuti jalan hina.
Bahkan pada saat sakit dengan penderitaan berat,
keteguhan mendorongnya untuk mempertahankan kegigihannya.
* * * * *
Labels:
Cerita - Sang Buddha
Sanghaguna
Di dalam Anguttara Nikaya, Tikanipata 20/267,
disebutkan tentang sifat-sifat mulia Sangha, yang disebut Sanghaguna.
Ada 9 jenis Sanghaguna, yaitu sebagai berikut.
1. Supatipanno
Bertindak/berkelakuan baik
2. Ujupatipanno
Bertindak jujur / lurus
3. Ñayapatipanno
Bertindak benar (berjalan di 'jalan' yang benar, yang mengarah pada perealisasian Nibbâna)
disebutkan tentang sifat-sifat mulia Sangha, yang disebut Sanghaguna.
Ada 9 jenis Sanghaguna, yaitu sebagai berikut.
1. Supatipanno
Bertindak/berkelakuan baik
2. Ujupatipanno
Bertindak jujur / lurus
3. Ñayapatipanno
Bertindak benar (berjalan di 'jalan' yang benar, yang mengarah pada perealisasian Nibbâna)
Labels:
Dhamma
Dhammaguna
Di dalam Anguttara Nikaya Tikanipata 20/266,
disebutkan tentang sifat Dhamma, atau Dhammaguna.
Ada 6 Dhammaguna, yakni sebagai berikut.
1. Svâkkhâto bhagavatâ dhammo
Dhamma Ajaran Sang Bhagava telah sempurna dibabarkan.
2. Sanditthiko
Berada sangat dekat (kesunyataan yang dapat dilihat dan dilaksanakan dengan kekuatan sendiri).
3. Akâliko
Tak ada jeda waktu atau tak lapuk oleh waktu.
disebutkan tentang sifat Dhamma, atau Dhammaguna.
Ada 6 Dhammaguna, yakni sebagai berikut.
1. Svâkkhâto bhagavatâ dhammo
Dhamma Ajaran Sang Bhagava telah sempurna dibabarkan.
2. Sanditthiko
Berada sangat dekat (kesunyataan yang dapat dilihat dan dilaksanakan dengan kekuatan sendiri).
3. Akâliko
Tak ada jeda waktu atau tak lapuk oleh waktu.
Labels:
Dhamma
Sembilan Buddhaguna
Di dalam Anguttara Nikaya Tikanipata 20/265,
disebutkan tentang sifat-sifat mulia Sang Buddha, atau disebut Buddhaguna.
Ada sembilan Buddhaguna, yaitu sebagai berikut.
1. Araham
Manusia suci yang terbebas dari kekotoran batin.
2. Sammâsambuddho
Manusia yang mencapai penerangan sempurna dengan usaha sendiri.
3. Vijjâcaranasampanno
Mempunyai penglihatan jernih yang sempurna dan tindak-tanduk bajik yang juga sempurna.
disebutkan tentang sifat-sifat mulia Sang Buddha, atau disebut Buddhaguna.
Ada sembilan Buddhaguna, yaitu sebagai berikut.
1. Araham
Manusia suci yang terbebas dari kekotoran batin.
2. Sammâsambuddho
Manusia yang mencapai penerangan sempurna dengan usaha sendiri.
3. Vijjâcaranasampanno
Mempunyai penglihatan jernih yang sempurna dan tindak-tanduk bajik yang juga sempurna.
Labels:
Dhamma
Arti Tiratana ?
Apa itu Tiratana?
Kata Tiratana terdiri dari kata Ti,
yang artinya tiga dan Ratana,
yang artinya permata/mustika;
yang maknanya sangat berharga.
Jadi, arti Tira-tana secara keseluruhan adalah Tiga Permata (Tiga Mustika)
yang nilainya tidak bisa diukur;
karena merupakan sesuatu yang agung, luhur, mulia,
yang sangat penting untuk dimengerti (dipahami) dan diyakini oleh umat Buddha.
Sesuai dengan arti katanya, yaitu Tiga Mustika atau Tiga Permata,
maka isi Tiratana memang terdiri dari 3 permata atau tiga Ratana, yaitu:
Buddha Ratana, Dhamma Ratana, dan Sangha Ratana.
Kata Tiratana terdiri dari kata Ti,
yang artinya tiga dan Ratana,
yang artinya permata/mustika;
yang maknanya sangat berharga.
Jadi, arti Tira-tana secara keseluruhan adalah Tiga Permata (Tiga Mustika)
yang nilainya tidak bisa diukur;
karena merupakan sesuatu yang agung, luhur, mulia,
yang sangat penting untuk dimengerti (dipahami) dan diyakini oleh umat Buddha.
Sesuai dengan arti katanya, yaitu Tiga Mustika atau Tiga Permata,
maka isi Tiratana memang terdiri dari 3 permata atau tiga Ratana, yaitu:
Buddha Ratana, Dhamma Ratana, dan Sangha Ratana.
Labels:
Dhamma
Arti Buddha
Arti Buddha (dalam Khuddaka Nikaya) adalah:
1. Dia Sang Penemu (Bujjhita) Kebenaran
2. Ia yang telah mencapai Penerangan Sempurna
3. Ia yang memberikan penerangan (Bodhita) dari generasi ke generasi
4. Ia yang telah mencapai kesempurnaan melalui 'penembusan', sempurna penglihatanNya,
dan mencapai kesempurnaan tanpa bantuan siapapun.
1. Dia Sang Penemu (Bujjhita) Kebenaran
2. Ia yang telah mencapai Penerangan Sempurna
3. Ia yang memberikan penerangan (Bodhita) dari generasi ke generasi
4. Ia yang telah mencapai kesempurnaan melalui 'penembusan', sempurna penglihatanNya,
dan mencapai kesempurnaan tanpa bantuan siapapun.
Labels:
Dhamma
01 Juni 2012
Sila Musavada - Tentang Ucapan
Tiap Puja Bakti kita menjalankan ritual menguncarkan Pancasila
sebagi janji melatih diri menghindari perbuatan buruk,
yang antara lain Musāvādā ( berbohong atau cerita yang tidak benar ).
Pengendalian diri sangatlah penting.
1. Pisunavācā,
fitnah, umpat, ucapan dengki yang bertujuan memperburuk orang lain atau memecah belah persahabatan.
sebagi janji melatih diri menghindari perbuatan buruk,
yang antara lain Musāvādā ( berbohong atau cerita yang tidak benar ).
Pengendalian diri sangatlah penting.
1. Pisunavācā,
fitnah, umpat, ucapan dengki yang bertujuan memperburuk orang lain atau memecah belah persahabatan.
2. Pharusavācā,
omong kasar.
Menggunakan kata-kata kasar yang menyakitkan hati atau merendahkan, menghina orang lain.
omong kasar.
Menggunakan kata-kata kasar yang menyakitkan hati atau merendahkan, menghina orang lain.
3. Samphappalāpavācā,
Menyombongkan diri dan membual atas fakta yang tidak benar dan orang percaya omongannya.
* * * * *
Labels:
Dhamma
Error Messages - Incompatible Server Version When Restore Database
Apply To :
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
Error Messages :
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2
Error Messages :